Getting less than six hours of sleep per night may make you dehydrated, concludes study
02/04/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
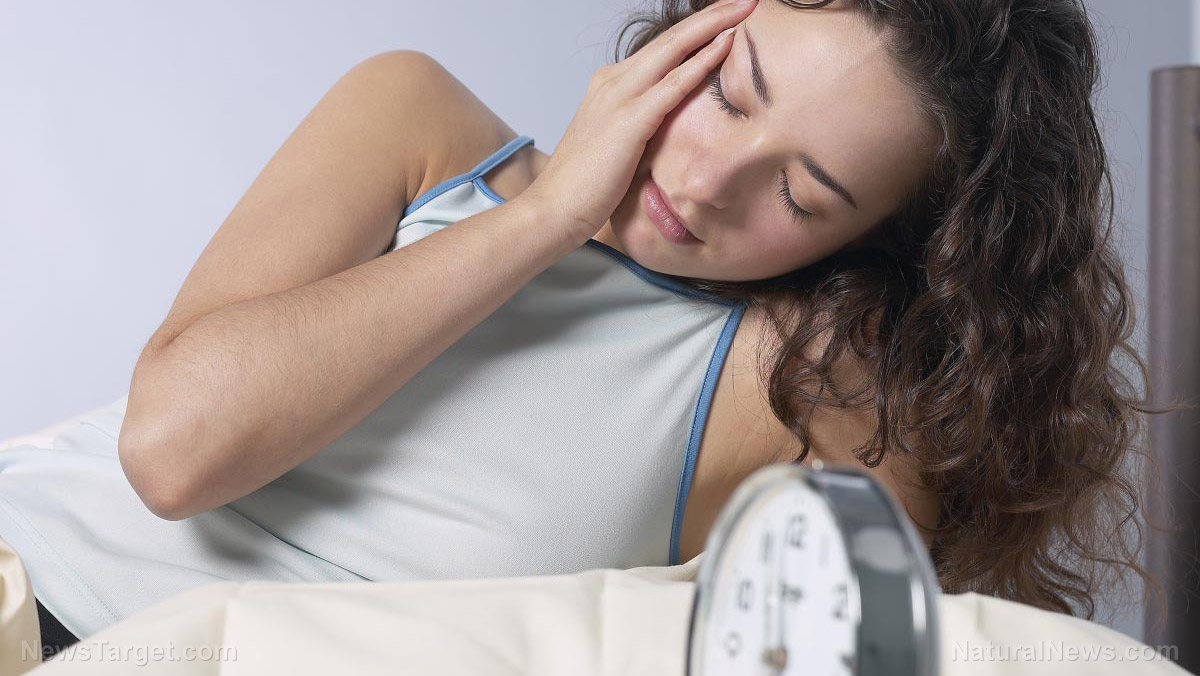

It is often recommended for adults to have seven to eight hours of sleep each day for good health. However, some people stay up late at night to work, study, or even have fun. For some, it could be due to medical reasons like sleeping problems.
No matter the reason, studies have shown that not having a good night’s sleep takes a toll on their health.
One of the consequences of sleeping for shorter hours, particularly six hours or less, is having a greater chance of being dehydrated, according to a study published in the journal Sleep.
Dehydration disrupts various systems and functions of the body, such as cognition, mood, physical performance, and many more. If dehydration is prolonged, it can result in more serious problems, such as an increased risk of urinary tract infections and kidney stones. So, if you feel unwell or tired the day after having a shorter sleep, it may be due to dehydration, and not poor sleep alone. With these findings, the study suggests for people to drink more water. (Related: Dehydration causes your brain SWELL, making it harder for you to complete everyday tasks.)
Carried out by researchers from Penn State University, the study examined the effect of sleep on hydration status and risk of dehydration in American and Chinese adults. The researchers analyzed a total of three samples with over 20,000 adults; two samples of adults through the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and one sample of adults through the Chinese Kailuan Study.
The researchers asked the participants about their sleeping habits through a survey. To measure the hydration of the participants, the researchers collected urine samples, which serve as biomarkers for hydration, from the participants.
The results showed that those who reported having six hours of sleep had dramatically more concentrated urine and 16 to 59 greater chances of being dehydrated compared to those who reported having eight hours of sleep regularly at night.
Penn State researchers believe that this may be due to the way the hormonal system of the body regulates hydration. Vasopressin, which is a hormone that helps regulate the body’s hydration status, is released both more rapidly and later on in the sleep cycle.
“So, if you’re waking up earlier, you might miss that window in which more of the hormone is released, causing a disruption in the body’s hydration,” explained Asher Rosinger, the study’s lead author and an assistant professor of biobehavioral health at Penn State.
Why do you need to get enough sleep?
It can’t be stressed enough: Sleep plays a role in many bodily functions. During sleep, the brain signals the body to release hormones and compounds that help:
- Reduce the risk of death from all causes: A review of 16 studies that cover over 1.3 million people and more than 100,000 deaths within 25 years revealed that people who generally slept for less than six hours a day had 12 percent higher risk of dying early.
- Regulate your appetite: Sleep deprivation can elevate the body’s energy needs. Movement and need for calories are reduced at night. However, when you lack sleep, your brain will release chemicals to signal hunger, resulting in eating more, exercising less, and gaining weight.
- Support the immune system: Cytokines are compounds released by the immune system during sleep. Some of these help the immune system in fighting inflammation and infection. However, when you are sleep-deprived, there are also not enough cytokines to protect you from diseases.
- Strengthen your memory: Sleep helps you focus and retains your memory. So, when you lack sleep, you are more likely to have a hard time focusing and remembering things. Your judgment may also be impaired.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: dehydrated, dehydration, hydration, sleep, sleep deprivation, sleepless night, water intake